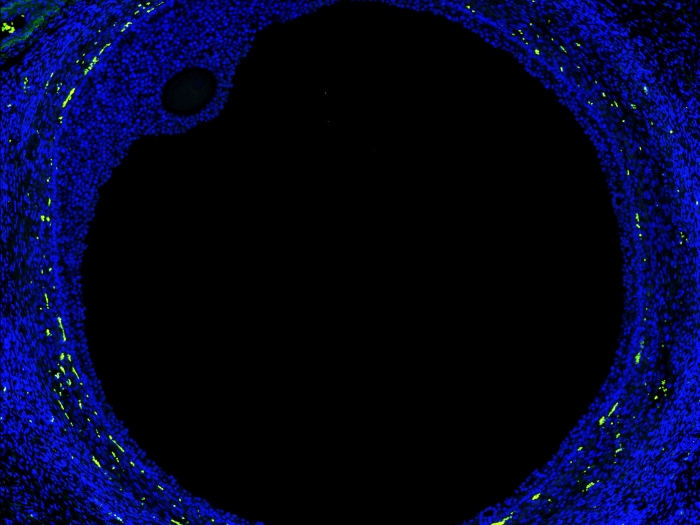
Molecular changes in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease could serve as potential therapeutic targets to halt the cells’ progression to liver cancer.
11:00 AM
Author |
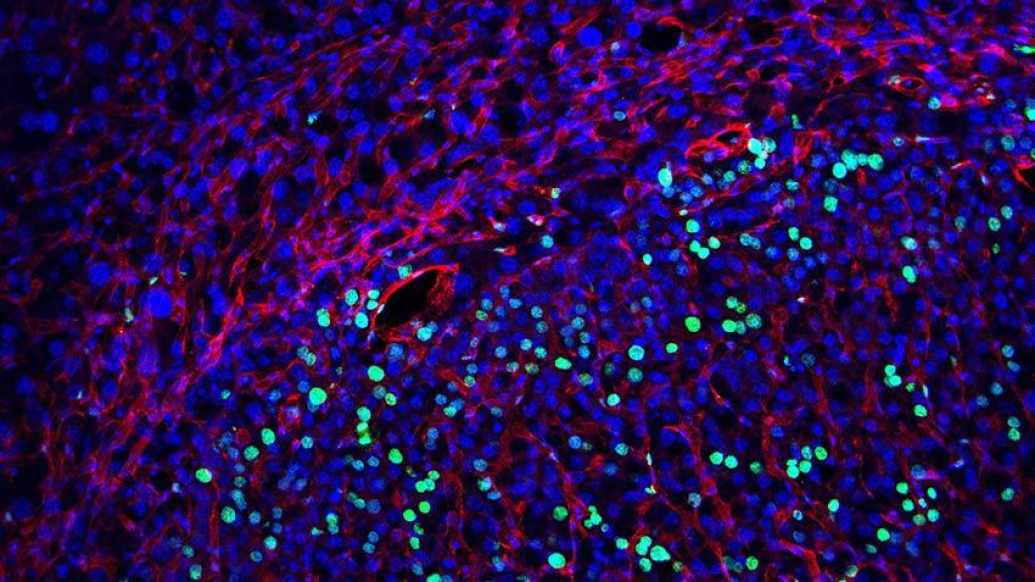
A hormone secreted by fat cells can restrain the growth of liver tumors in mice, according to a new study from the University of Michigan Life Sciences Institute. The findings offer a proof-of-concept for developing therapies against hepatocellular carcinoma, the most common form of liver cancer.
Jiandie Lin, Ph.D., and his team use mice as a model to study how molecular and cellular changes are affected by nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and how these changes consequently lead to the progression of this disease. While it begins as a relatively benign accumulation of fat in the liver, the disorder can develop into nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, which increases the risk for liver cancer.
The liver contains scores of different cell types, including various immune cells. Using single-cell RNA sequencing, a technology for probing gene expression of individual cells within complex tissues, Lin and his team previously constructed a liver cell atlas and a blueprint of intercellular signaling in healthy and NASH mouse livers.
For this latest study in Cell Metabolism, the scientists wanted to identify specific molecular changes in the NASH state that disrupt balance and interactions of these cell types, as potential therapeutic targets to reverse the progression from NASH to cancer.
"Liver cancer in NASH patients is different from cancers caused by viral hepatitis, in that it often develops in the absence of liver cirrhosis," explained Lin, a faculty member at the U-M Life Sciences Institute and the study's senior author. "We suspect that different disease mechanisms may be engaged in NASH-related liver cancer."
Like Podcasts? Add the Michigan Medicine News Break on Spotify, Apple Podcasts or anywhere you listen to podcasts.
Lin and his colleagues observed changes in two types of immune cells in particular that appear to contribute to the development of HCC. In mouse livers with NASH, T cells — the immune cells that normally fight infected or damaged cells, such as cancerous cells — showed hallmarks of functional impairments. At the same time, the team found that a second type of immune cell, called macrophages, acquired molecular features typically associated with cancers.
"These changes we saw in macrophages and T cells resemble the tumor microenvironment, but they are happening even before any cancer becomes apparent," said Lin, who is also a professor of cell and developmental biology at the U-M Medical School. "It gives us a hint that maybe these changes in the liver microenvironment could provide fertile ground for liver cancer cells to appear and grow. It almost looks like the liver, once it develops NASH, is already preparing for cancer cells to thrive."
Reversing liver disease, with a hormone from fat
The team also identified a hormone that serves as a checkpoint for disease progression, and it appears to have potential as a treatment: neuregulin 4, or NRG4.
Lin's team previously revealed that NRG4—a hormone that is secreted primarily by fat cells—can protect mouse livers against NASH, and that a decrease or loss of this hormone lead to more severe levels of liver disease.
Now, the team has found that the hormone can suppress HCC in NASH mice. Their findings show that mice lacking NRG4 develop more severe NASH and more liver tumors than mice with normal levels of NRG4.
When the scientists boosted NRG levels in mice—either by genetically elevating the expression of NRG4 in fat tissues or by treating mice with a recombinant NRG4 fusion—the increased levels of NRG4 suppressed NASH liver cancer progression.
"A lot of studies on liver cancer focus on the cancerous liver cells themselves: how they proliferate and how they evade the immune system," Lin said. "But our findings break out of this liver-centered framework, showing a fat-derived hormone could actually reprogram the liver environment and have very big impact on liver cancer development."
More research is needed before NRG4 can be pursued as a therapeutic for HCC. Lin and his team now plan to investigate approaches for improving the hormone's effectiveness and to better understand the nature underlying its regulation of macrophages and T cells in the liver.
Live your healthiest life: Get tips from top experts weekly. Subscribe to the Michigan Health blog newsletter
Headlines from the frontlines: The power of scientific discovery harnessed and delivered to your inbox every week. Subscribe to the Michigan Health Lab blog newsletter
Study authors include Peng Zhang, Zhimin Chen, Henry Kuang, Tongyu Liu, Jiaqiang Zhu, Linkang Zhou, Qiuyu Wang, Xuelian Xiong, Ziyi Meng, Xiaoxue Qiu, Ramiah Jacks, Lu Liu, Siming Li, Carey N. Lumeng, Qing Li, Xiang Zhou and Jiandie D. Lin of the University of Michigan.
This research was supported by funding from the National Institutes of Health and a pilot grant from the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center.
Paper cited: "Neuregulin 4 suppresses NASH-associated liver cancer through restraining tumor-prone liver microenvironment," Cell Metabolism. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.07.010

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!