Investigators also found that diabetes complications are linked to these changes in the brain
5:00 AM
Author |
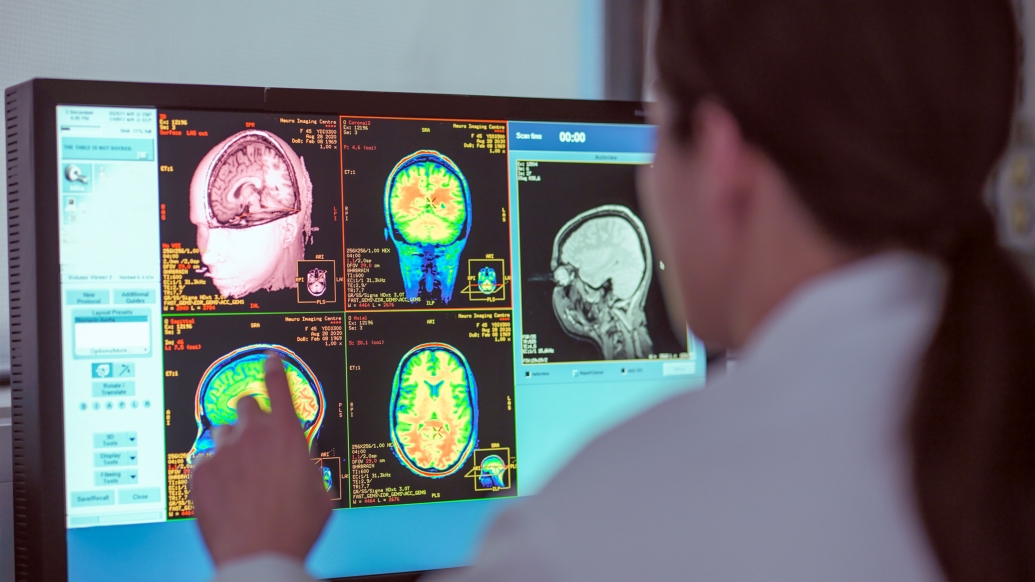
The longer a person has type 2 diabetes, the more likely they may be to experience changes in brain structure, a Michigan Medicine study finds.
Researchers analyzing data from 51 middle-aged Pima American Indians living with type 2 diabetes used a series of memory and language tests developed by the National Institutes of Health, called the NIH Toolbox Cognitive Battery, as well as MRI, to determine the relationship between diabetes, cognition and makeup of the brain.
SEE ALSO: Lipids in blood predict nerve damage risk among patients with type 2 diabetes
Brain imaging suggested that study participants with longer durations of type 2 diabetes had decreased mean cortical thickness and gray matter volumes, and an increased volume of white matter hyperintensities.
The MRI results, researchers say, indicate the negative effects longstanding diabetes may have on brain health outcomes and emphasize the importance of preventing early onset type 2 diabetes.
Cognition in study participants with type 2 diabetes did not differ compared to those without the condition.
Results are published in Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology.
“This is among the first times that alterations of the brain’s structure have been associated with duration of diabetes,” said first author Evan Reynolds, Ph.D., research fellow and lead statistician for the NeuroNetwork for Emerging Therapies at Michigan Medicine
“Although we did not find reduced cognition through the NIH Toolbox, this might not give the entire picture. The fact that we saw negative changes in the brain itself provides evidence for the need for early screening for cognitive disorders in patients with type 2 diabetes to improve patient care and quality of life.”
Investigators also found that diabetes complications, such as chronic kidney disease and damage to the nerves in the heart and blood vessels, are linked to structural changes to the brain.
This falls in line with another of the team’s studies, which found that diabetic complications increased the odds of developing a cognitive disorder by 2.45 times in 40 to 60-year-olds.
Researchers were surprised that neuropathy, by which up to 50% of people with diabetes can be affected, was not associated with cognitive function in the study.
“This study is critical to our understanding of how diabetes affects brain health and lays the groundwork for a larger, longitudinal study addressing how persons with diabetes can maintain a healthy brain,” said senior author Eva Feldman, M.D., Ph.D., James W. Albers Distinguished Professor at U-M, the Russell N. DeJong Professor of Neurology at U-M Medical School and director of the NeuroNetwork for Emerging Therapies at Michigan Medicine.
“Regardless of the underlying mechanisms, preventing these conditions in people with type 2 diabetes is critical to maintaining brain health. Educating the public on the risks that diabetes poses to a preserving a healthy brain is part of our mission.”
Additional authors include Kristen Votruba, Ph.D., Rodica Pop-Busui, M.D., Ph.D., and Brian C. Callaghan, M.D., all of Michigan Medicine, Clifford R. Jack, M.D., Gregory M. Preboske, Robert I. Reid, Ph.D., all of Mayo Clinic, Richard Beare, Ph.D., of Monash University, and Camille Waseta, and Robert G. Nelson, M.D., Ph.D., both of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Pop-Busui receives research support from Novo Nordisk.
Callaghan consults for DynaMed, receives research support from the American Academy of Neurology and performs medical legal consultations including consultations for the Vaccine Injury Compensation Program.
This research was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and the National Institute on Aging at the National Institutes of Health (grants (K99DK129785, R01DK107956, U01DK119083, 1U01 DK0945157, R01DK116723, R01DK115687, U24DK115255, R01DK130913 and U01AG057562), the Alexander Family Professorship at Mayo Clinic, the JDRF Center of Excellence at the University of Michigan, the Robert E. Nederlander Sr. Program for Alzheimer’s Research, the Andrea and Lawrence A. Wolfe Brain Health Initiative Fund, the A. Alfred Taubman Medical Research Institute, and the NeuroNetwork for Emerging Therapies.
The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Paper cited: “Association between brain health outcomes and metabolic risk factors in persons with diabetes,” Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology. DOI: 10.1002/acn3.5185

Explore a variety of health care news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!





