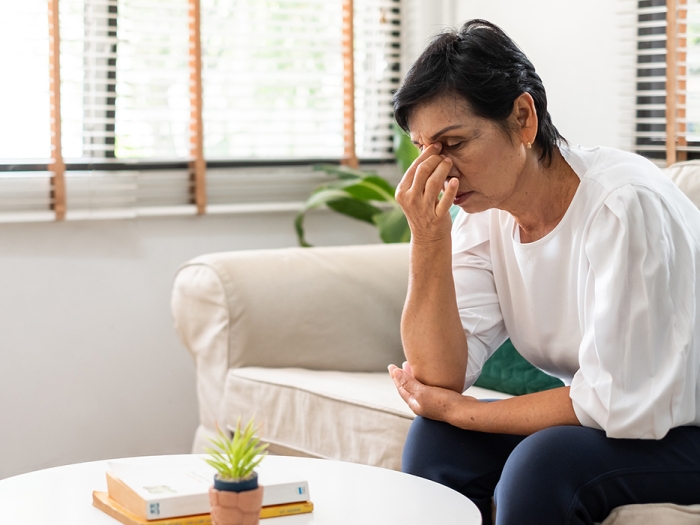
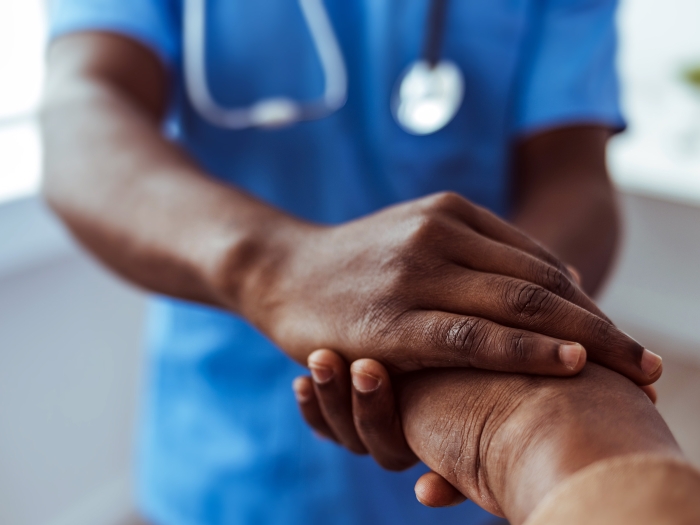
Postponing procedures during the pandemic sparked anxiety and fear among patients, with many concerned about dying of their conditions before getting surgery.
2:51 PM
Author |
"And then the coronavirus hit. Everything came to a stop. I couldn't have my surgery." -- Sophia (a pseudonym), 56 years old.
In March 2020, when the pandemic hit, everything slowed, including non-essential medical procedures such as elective surgeries, to reduce the spread of the coronavirus.
Six weeks later, Mary Byrnes, Ph.D., an assistant research scientist in the Department of Surgery at Michigan Medicine, began calling Frankel Cardiovascular Center patients whose surgeries had been canceled or delayed. She wanted to hear about their experiences — what undergoing surgery meant to them, how postponing their operations had affected them, whether the existence of the coronavirus complicated how they felt about their bodies and about surgery.
Over the next 10 days, she heard stories of fear: "I'm literally afraid to have my surgery now, and I'm just going day by day on prayer and hoping...that I don't have anything fatal attack my system."
And suffering: "This last week... I've just been struggling. And I...I don't know if it's more symptoms or anxiety or whatever, but...I'm just ready to get this behind me and hopefully live a better life."
As well as altruism: "As much as I want it done, those nurses are overwhelmed right now. They don't need another person in there. Let's hope this starts calming down, and they get a breather before... people are coming in for surgery."
SEE ALSO: How to Improve the Surgery Backlog During COVID-19
Collectively, the 47 interviews Byrnes conducted — compiled for a study recently published in Medical Care — illustrate the profound impact of postponing cardiovascular surgeries due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
"There's been other work coming out that said patients don't really care about delaying their surgeries," says Byrnes, the first author of the study. "But the heart is a different type of organ that has a lot of emotions wrapped around it. It's literary even."
"And even though these were elective surgeries," she adds, "they were serious operations where people were literally having their chests cracked open, and so there was a lot of mental preparation to confront that in the first place. Ultimately, they viewed surgery as a cure, so the unknowing about whether it would happen was problematic for them."
Facing their own mortality
Despite all the uncertainty, many patients preferred to wait to undergo surgery in an effort to avoid catching COVID-19. Some thought they were likely to die of their cardiovascular conditions before their operations could take place, yet they favored passing away of "the devil they knew" over "the devil they didn't," says Byrnes.
In the past year, more Americans have died than would be expected, even when accounting for those who have passed away from COVID-19 or related complications. One of the driving factors may be certain cardiovascular conditions, namely ischemic heart disease — when narrowed coronary arteries cause heart problems — and illness related to high blood pressure. States that experienced COVID-19 surges early in the pandemic, including New York and Michigan, also saw a spike in deaths linked to these issues, potentially because patients avoided health care during those periods.
"Patients are suffering even though we don't see them," Byrnes says. "We have to think about our policies and how we talk to patients in terms of the fact that they think they're going to die — and they might."
What surgeons can learn
As Michigan Medicine and other local health systems begin to delay a small number of surgeries again, thanks to the latest COVID-19 surge in Michigan, this study's findings can inform the decisions hospital leadership makes and create an opportunity for additional communication with and support for cardiovascular patients.
"We need to be upfront and accessible," says Nicholas H. Osborne, M.D., the associate program director of vascular surgery at Michigan Medicine and the last author of the study. "Cancellations should be communicated directly to patients, and surgeons should be available to talk with patients to reassure them."
"As a healthcare system, we may also need to design and implement interventions, such as support systems or social work resources, to minimize the impact these delays have on the well-being of our patients," says Craig Brown, M.D., M.S., a general surgery resident at Michigan Medicine and an additional author of the study. "It is not simply an inconvenience to many of them, but rather has dramatic consequences and substantial psychological impacts on their wellbeing."
Additional authors included Ana C. De Roo, M.D., M.S., Matthew A. Corriere, M.D., M.S., Matthew A. Romano, M.D., Shinichi Fukuhara, M.D., and Karen M. Kim, M.D. Byrnes, Corriere, and Osborne are all members of the Center for Healthcare Outcomes and Policy. Brown and De Roo are CHOP fellows.
Paper cited: "Elective Surgical Delays due to COVID-19: The Patient Lived Experience," Medical Care. DOI: 10.1097/MLR.0000000000001503

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!





