Expert weighs in on why men struggle to discuss prostate cancer diagnosis
3:15 PM
Author |

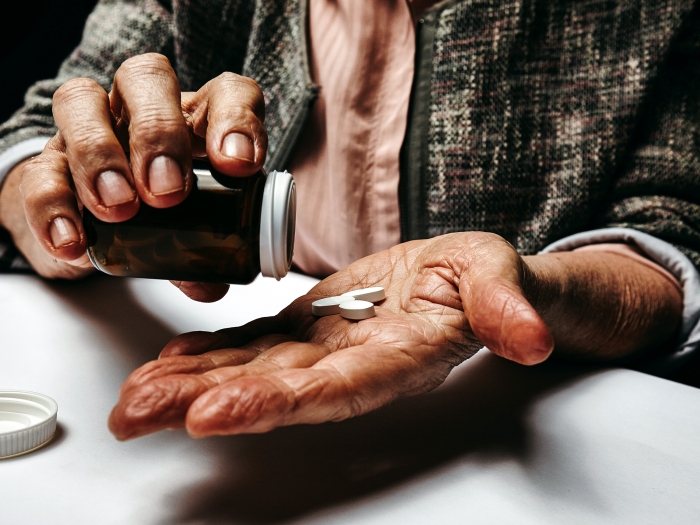
When U.S. Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin was diagnosed with prostate cancer, his illness was largely kept quiet from the public. Though Austin faced scrutiny for not being more forthcoming about his health, experts like Daniela Wittmann Ph.D., L.M.S.W. say prostate cancer is often difficult for men to discuss openly.
Wittmann answers some common questions about stigma surrounding this diagnosis, how it may impact patients and their families, where those struggling can get help, and ultimately how men can preserve their strength and dignity through this health care journey.
What is the stigma associated with prostate cancer?
Prostate cancer is a disease that is highly prevalent. One in eight men in the U.S. has a chance of being diagnosed with it in his lifetime. If the man is African American, the likelihood is higher, one in 6. Many men prefer to keep a cancer diagnosis private, often because they do not like attention for a vulnerability such as a life threatening illness. Culturally, men prefer to be and be seen as strong and capable. In the case of prostate cancer, there is the additional stigma of the treatment related side effects – urine leakage and erectile dysfunction after surgery. People used to think of prostate cancer as a cancer that would end a man’s sex life.
What kind of feelings does this evoke for patients?
Men may feel sad, frightened by a cancer diagnosis, fearful that it is life threatening, vulnerable, and/or embarrassed.
How can patients find help?
It is important for men to realize that prostate cancer is highly treatable, and over 98% of men survive 10 years if the cancer is diagnosed and treated early. Regarding the urinary and sexual side effects, 97% of men recover bladder control within a year, many much earlier. Physical therapy and pelvic floor rehabilitation helps with that process. Erectile dysfunction may improve over time, but even if it does not, men are able to use the assistance of medications or devices and return to sexual intimacy. Therefore, sexual rehabilitation restores the man’s ability to have a sex life after prostate cancer treatment. It is important to educate patients about the likelihood of survival and rehabilitation for the side effects of treatment so that they can feel confident that they will regain their quality of life. In the U.S., many men do not get education about the side effects and are not offered rehabilitation. This leaves them and their partners suffering with a lifelong impact on their lives. Organizations, such as the American Cancer Society and online resources such as Malecare and ZERO Prostate Cancer provide information and online support.
Do high profile cases like Austin’s help combat this stigma?
A man in Secretary Austin’s situation has an opportunity to inspire men to get screened for prostate cancer to save lives and be hopeful about getting their life back if they need to be treated. Anyone in a high level position can be a role model for being open, not embarrassed and matter of fact, which will encourage others to get help. However, in today’s political climate, being open about one’s vulnerability may be challenging to people in high positions.
Sign up for Health Lab newsletters today. Get medical tips from top experts and learn about new scientific discoveries every week by subscribing to Health Lab’s two newsletters, Health & Wellness and Research & Innovation.
Sign up for the Health Lab Podcast: Add us on Spotify, Apple Podcasts or wherever you get you listen to your favorite shows.

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!