Putting patients on aspirin following a knee replacement is a safe, cost-effective alternative to anticoagulants, U-M researchers find.
1:00 PM
Author |

When it comes to preventing blood clots after a knee replacement, good old aspirin may be just as effective as newer, more expensive drugs.
LISTEN UP: Add the new Michigan Medicine News Break to your Alexa-enabled device, or subscribe to our daily audio updates on iTunes, Google Play and Stitcher.
That swap could help reduce the cost of caring for the nearly 1 million Americans who have a knee fixed each year, Michigan Medicine researchers say.
After knee surgery, there's a risk of blood clots in the legs or lungs. So it's routine for patients to take clot-preventing drugs for some time afterward.
Some doctors choose powerful anti-clotting drugs like heparin (Lovenox) and rivaroxaban (Xarelto), but it hasn't been clear whether these expensive prescription drugs work any better than cheap, readily available aspirin.
"Aspirin alone may provide similar protection compared to anticoagulation treatments," says Brian R. Hallstrom, M.D., an orthopaedic surgeon and associate chair for quality and safety at the University of Michigan Department of Orthopaedic Surgery.
Hallstrom is the lead author of a new study published in JAMA Surgery that found few patients developed a blood clot after surgery, and those patients on aspirin fared just as well as those on anticoagulants.
Aspirin is easy to take . . . patients can get it over the counter for pennies, while the other anticoagulants require monitoring, injections, frequent dose adjustments and are extremely expensive.Brian R. Hallstrom, M.D.
Aspirin use growing
During the two-year study period from 2013 to 2015, aspirin use rose from 10 percent to 50 percent among the patients cared for by orthopaedic surgeons in the Michigan Arthroplasty Registry Collaborative Quality Initiative, a statewide effort to give patients the best possible recovery and outcomes after hip and knee replacements.
MORE FROM THE LAB: Subscribe to our weekly newsletter
Since then, the shift has become even more distinct: Aspirin prescribing has risen to 70 percent among Michigan surgeons, says Hallstrom, who is co-director of the initiative and a health services researcher at U-M's Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation.
Based on the experience of 41,537 Michigan patients undergoing knee replacement, the study may further the debate about the routine use of aspirin for clot prevention.
A recent Canadian study looked at the issue, but the analysis had a caveat: Each of the more than 3,400 clinical trial patients received rivaroxaban the first five days after surgery. After that, they continued with the drug or switched to aspirin.
The new U-M study suggests patients may be adequately protected if they take aspirin alone from day one.
"This study is truly a real-world experience of what happened in Michigan when the majority of surgeons switched to aspirin," Hallstrom says. "The incidence of blood clots, pulmonary embolus and death did not increase despite this dramatic change in practice."
Shifting procedure and dialogue
Over the past decade, surgeons have turned away from powerful anticoagulants and toward aspirin used in addition to nondrug improvements such as compression devices for thwarting clots.
These days, most patients have a generally low risk of blood clots after knee replacement for a number of reasons. Those reasons include shorter surgical times, less invasive procedures and use of regional anesthesia that allows early mobilization after surgery, Hallstrom says. Some patients are even going home the same day.
SEE ALSO: Study: Apixaban Blood Thinner May Be Safer for Dialysis Patients with Afib
"The most important way to prevent blood clots is getting moving," says Hallstrom, noting that people are at risk for blood clots when they sit or lie in one position for too long, such as on an airplane or a hospital bed.
Still, pharmaceutical recommendations vary.
The critical care specialists who make up the American College of Chest Physicians favor heparin to reduce the risk of blood clots, while the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons guidelines state that no one drug is better than another for preventing clots.
Advantages of aspirin
The U-M study involved patients undergoing knee replacement surgery at any of the 29 Michigan hospitals in the surgical quality group. One-third of the patients took aspirin alone; 54 percent took only an anticoagulant; and 13 percent took an aspirin/anticoagulant combination.
Over three months, just 1.16 percent of aspirin patients developed a serious blood clot. That was true for 1.42 percent of anticoagulant patients, according to the Michigan study. This was not statistically different.
So, neither drug appeared better than the other — but aspirin has some obvious advantages.
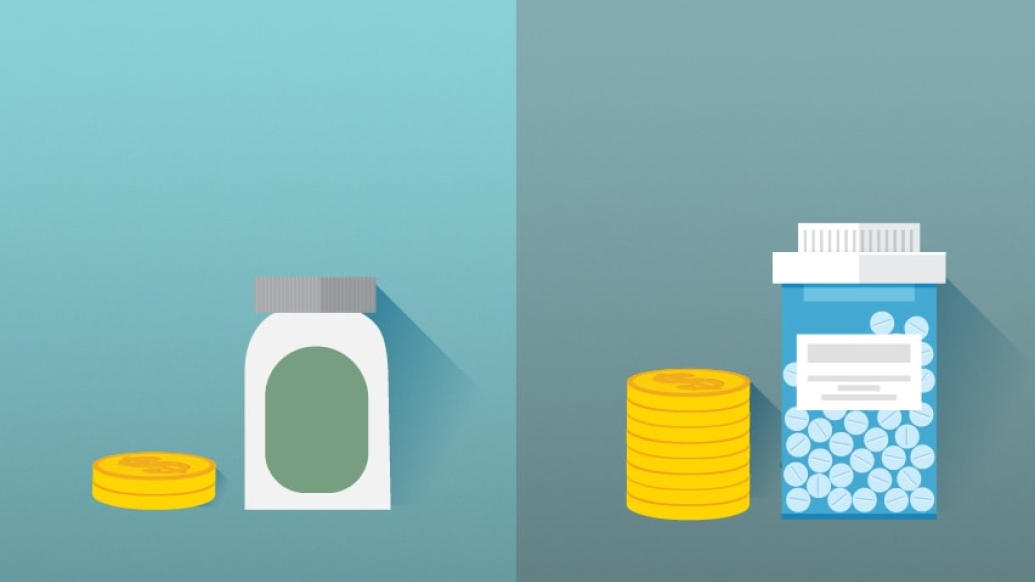
"Aspirin is easy to take and much less expensive," Hallstrom says. "Patients can get it over the counter for pennies, while the other anticoagulants require monitoring, injections, frequent dose adjustments and are extremely expensive."
The reported cost for a 30-day supply of rivaroxaban is approximately $379 to $450; heparin is estimated at $450 to $890. Although warfarin costs a few dollars for a 30-day supply, its cost approaches that of the other anticoagulants when doctor visits for monitoring are factored in, Hallstrom says.
In contrast, aspirin costs approximately $2 a month.
The study suggests most patients can have just aspirin without increasing the risk for venous thromboembolism, but doctors need to consider factors such as a patient's history of clots, obesity and ability to mobilize after surgery when determining the best measure for clot prevention, Hallstrom adds.

Explore a variety of health care news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!