A new retrospective study addresses the question of how often to screen for breast cancer, suggesting benefits to yearly screening.
10:40 AM
Author |
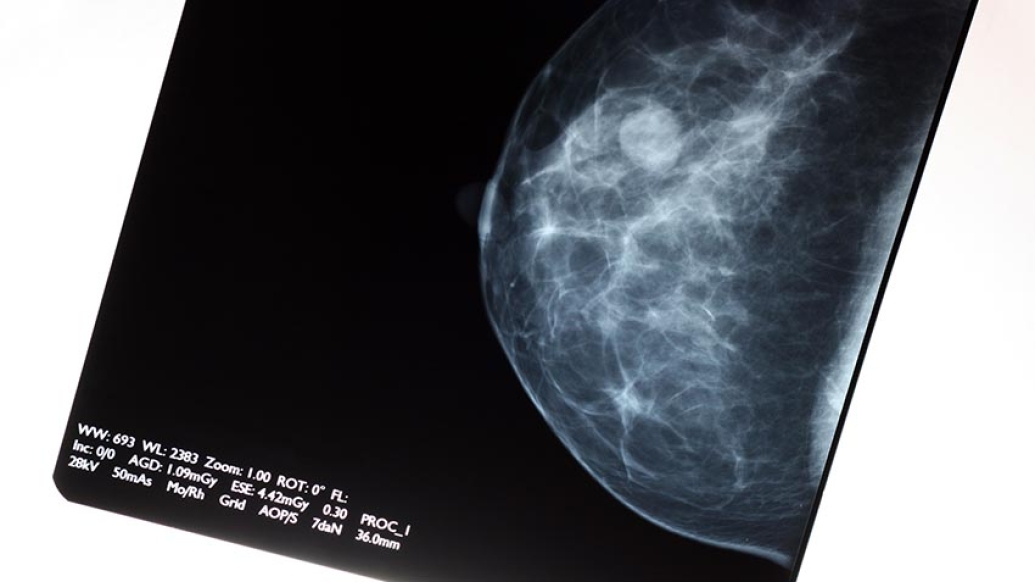
How often should women get a mammogram? A new study makes a case for getting screened every year instead of every other year.
Women diagnosed with breast cancer after receiving yearly mammograms had smaller tumors and less-advanced disease than women who had mammograms every other year, researchers from the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center found.
The researchers reviewed breast cancer patient records and identified 232 women who were diagnosed between ages 40-84, the age range for which mammography is recommended. Most women, 86%, had annual mammograms, while 14% had a mammogram every other year.
MORE FROM THE LAB: Subscribe to our weekly newsletter
"Our study found that screening mammography performed once a year resulted in less advance stage disease in patients diagnosed with breast cancer," says study author Sarah Moorman, M.D., a radiology resident at Michigan Medicine. "These results may help women make informed decisions about the frequency of breast cancer screening."
Moorman will present the study results Dec. 4 at the Radiological Society of North America Annual Meeting.
While the value of mammography in detecting breast cancer is widely accepted among professional societies and government agencies, there's disagreement about how frequently women should be screened.
"Recommendations for frequency of screening mammography remain variable among professional organizations. This data suggests screening mammography performed at less than annual frequency may result in increased morbidity for women diagnosed with breast cancer," says study author Akshat C. Pujara, M.D., assistant professor of radiology at Michigan Medicine.
In this study, those who had an annual screening had significantly lower incidence of advanced stage disease and significantly smaller tumors compared to those who had biennial mammograms, the researchers found. There were also fewer incidences of cancer occurring between screening mammograms.
LISTEN UP: Add the new Michigan Medicine News Break to your Alexa-enabled device, or subscribe to our daily updates on iTunes, Google Play and Stitcher.
Annual screenings were also tied to trends showing less frequent use of treatments such as removal of lymph nodes or chemotherapy, compared to biennial screening. The findings held true when researchers looked only at post-menopausal women.
"Mammography is one of the few screening tools that has been proven to save lives," says study author Mark Helvie, M.D., Trygve O. Gabrielsen Collegiate Professor of Radiology and medical director of cancer center radiology at Michigan Medicine. "This study confirms the benefit of more frequent annual screening."

Explore a variety of health care news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!





