Your heart does a lot of work to keep the body going. Learn about the organ’s amazing power and the functions of its many parts.
7:00 AM
Author |
This story was updated on January 31, 2020.
Each day, the average human heart beats about 100,000 times, pumping 2,000 gallons of blood through the body.
That's a lot of work for an organ no bigger than a large fist and weighing 8 to 12 ounces.
LISTEN UP: Add the new Michigan Medicine News Break to your Alexa-enabled device, or subscribe to our daily audio updates on iTunes, Google Play and Stitcher.
In fact, the heart does more physical work than any other muscle over a lifetime.
Located between the lungs in the middle of the chest, the heart pumps blood through the network of arteries and veins known as the cardiovascular system. It pushes blood to the body's organs, tissues and cells.
Blood delivers oxygen and nutrients to every cell and removes the carbon dioxide and other waste products made by those cells.
Blood is carried from the heart to the rest of the body through a complex network of arteries, arterioles and capillaries. Blood is returned to the heart through venules and veins.
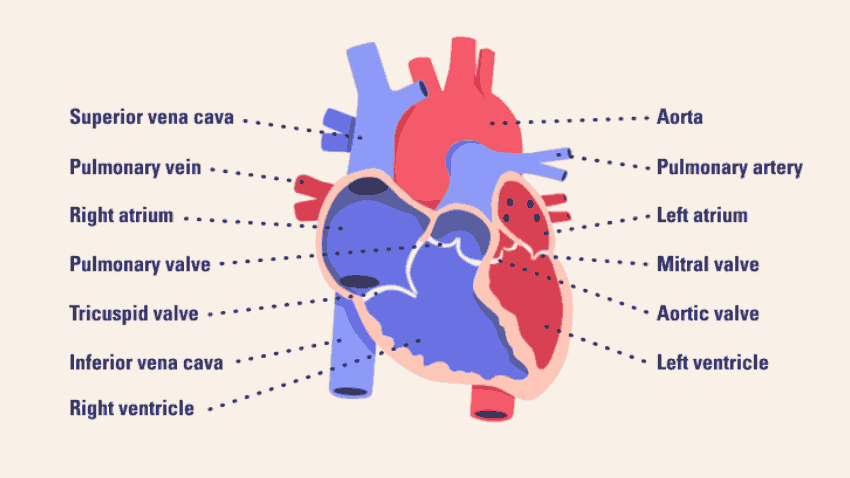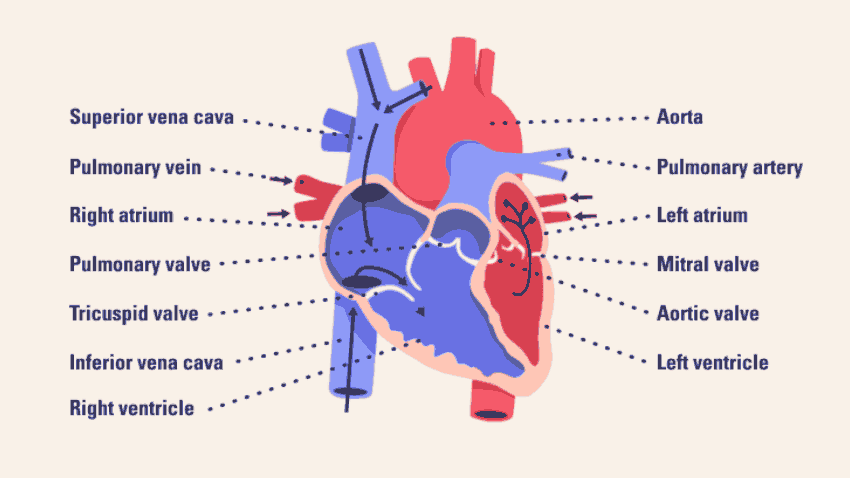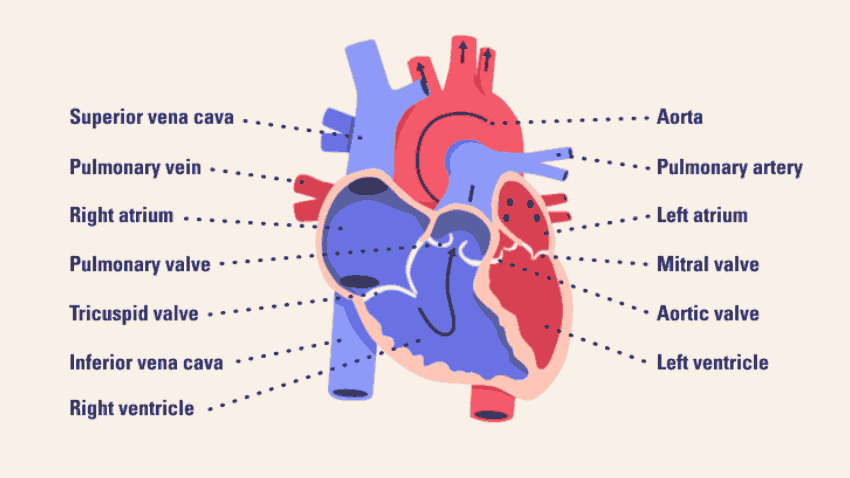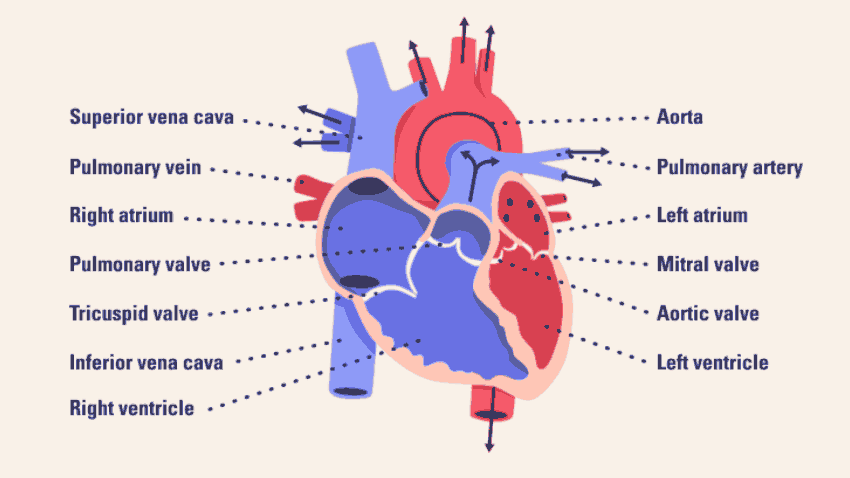
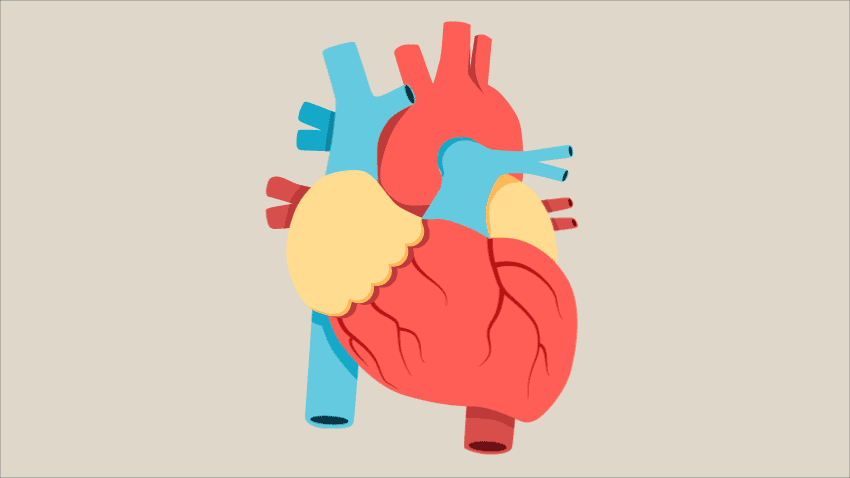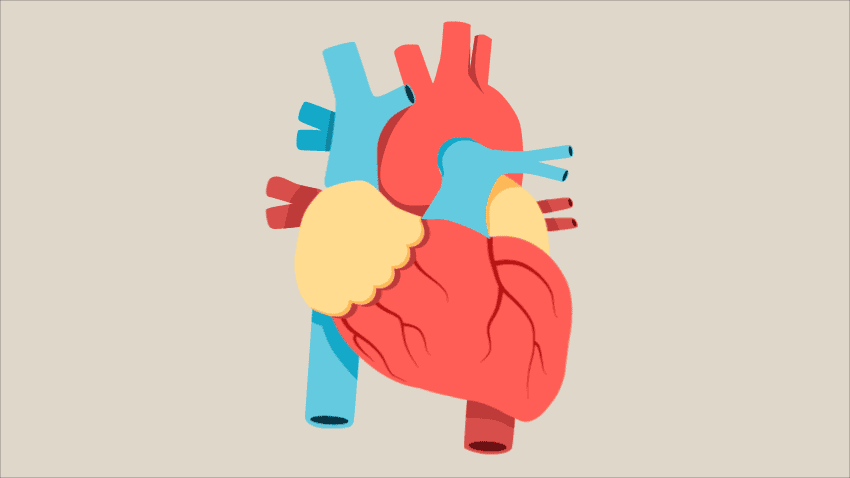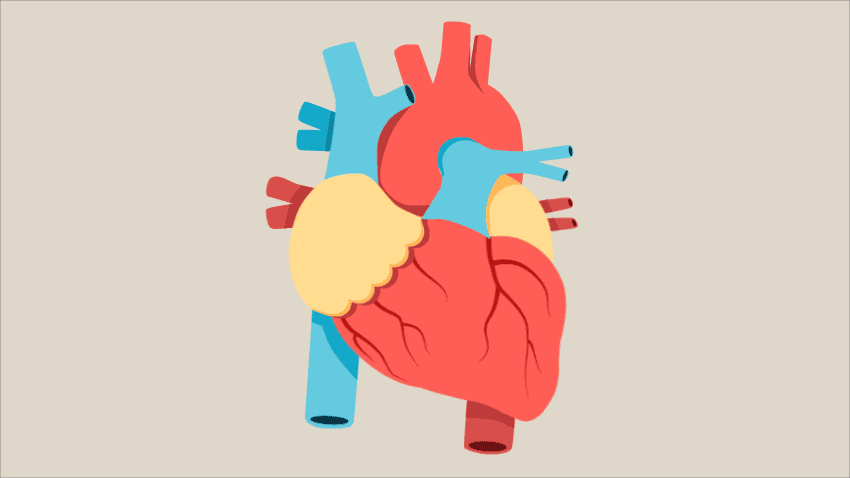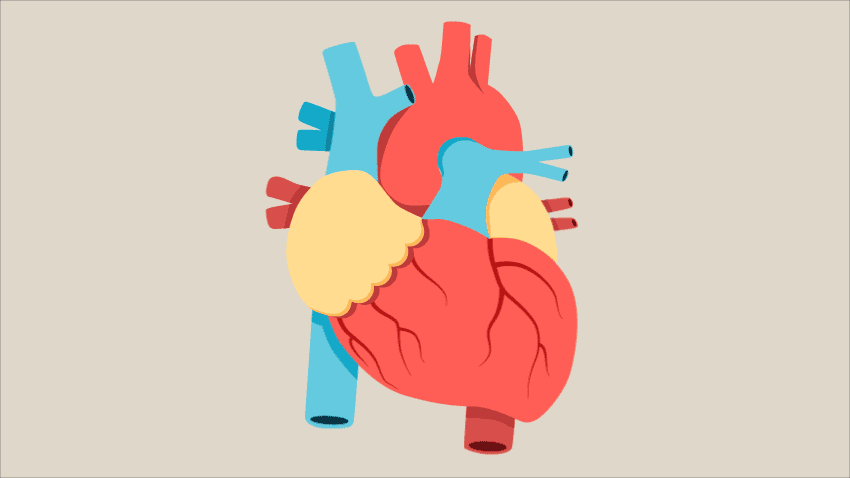
Parts of the human heart
The heart is made up of four chambers: two upper chambers known as the left atrium and right atrium and two lower chambers called the left and right ventricles.
MORE FROM MICHIGAN: Sign up for our weekly newsletter
It is also made up of four valves: the tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral and aortic valves.
-
The right atrium receives non-oxygenated blood from the body's largest veins — superior vena cava and inferior vena cava — and pumps it through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
-
The right ventricle pumps the blood through the pulmonary valve to the lungs, where it becomes oxygenated.
-
The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it through the mitral valve to the left ventricle.
-
The left ventricle pumps oxygen-rich blood through the aortic valve to the aorta and the rest of the body.
The coronary arteries run along the surface of the heart and provide oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle.
A web of nerve tissue also runs through the heart, conducting the complex signals that govern contraction and relaxation. A sac known as the pericardium surrounds the heart.
The outer layer of the pericardium surrounds the roots of the heart's major blood vessels, and the inner layer is attached to the heart muscle.

Explore a variety of health care news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!





