2:00 PM
Author |
ANN ARBOR — The University of Michigan Medical School will no longer participate in the annual U.S. News & World Report (USNWR) rankings of medical schools.
The criteria used by USNWR to rank medical schools has long been a concern at the University of Michigan and many medical schools across the country.
“The fundamental problem is that an aggregated score, based on many different dimensions, cannot possibly help students or others evaluate institutions with respect to their individual priorities,” said Marschall S. Runge, dean of the U-M Medical School, CEO of Michigan Medicine and executive vice president of medical affairs for the University of Michigan.
“Creating an overall ranking blurs each school’s individual attributes into a single score or rank that only reflects priorities set by USNWR itself.”
The U-M Medical School will no longer submit data for the USNWR medical school rankings. The decision was made after discussion and review with U-M and Medical School leaders, faculty, and students.
Runge said he and other medical schools' deans have worked for some time to encourage USNWR to change its ranking process.
“We made multiple suggestions to USNWR leadership urging change in their methodologies. Ultimately, these discussions yielded only minor revisions to the methodology used to rank medical schools,” Runge said.
“U-M Medical School remains committed to sharing data that might assist potential students in their decision making,” said Debra F. Weinstein, executive vice dean for academic affairs at the U-M Medical School and chief academic officer for Michigan Medicine.
“We understand that some students have used rankings to inform their choices. Sharing specific data points on our public website will help prospective students and others evaluate aspects of our school that are most important to them,” Weinstein said.
The U-M Medical School is the education division of Michigan Medicine, which is the academic medical center of the University of Michigan.
This decision does not relate to U-M Health’s participation in hospital or health system rankings, which may provide helpful information to patients and families. U-M Health is the clinical division of Michigan Medicine that includes five hospitals, more than 100 clinics and home care operations that handle more than 2.3 million outpatient visits a year.
About Michigan Medicine:
At Michigan Medicine, we advance health to serve Michigan and the world. We pursue excellence every day in our five hospitals, 125 clinics and home care operations that handle more than 2.3 million outpatient visits a year, as well as educate the next generation of physicians, health professionals and scientists in our U-M Medical School.
Michigan Medicine includes the U-M Medical School and University of Michigan Health, which includes the C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital, Von Voigtlander Women’s Hospital, University Hospital, the Frankel Cardiovascular Center, Kellogg Eye Center, University of Michigan Health West and the Rogel Cancer Center. The U-M Medical School is one of the nation's biomedical research powerhouses, with total research funding of more than $500 million.
More information is available at www.med.umich.edu/

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
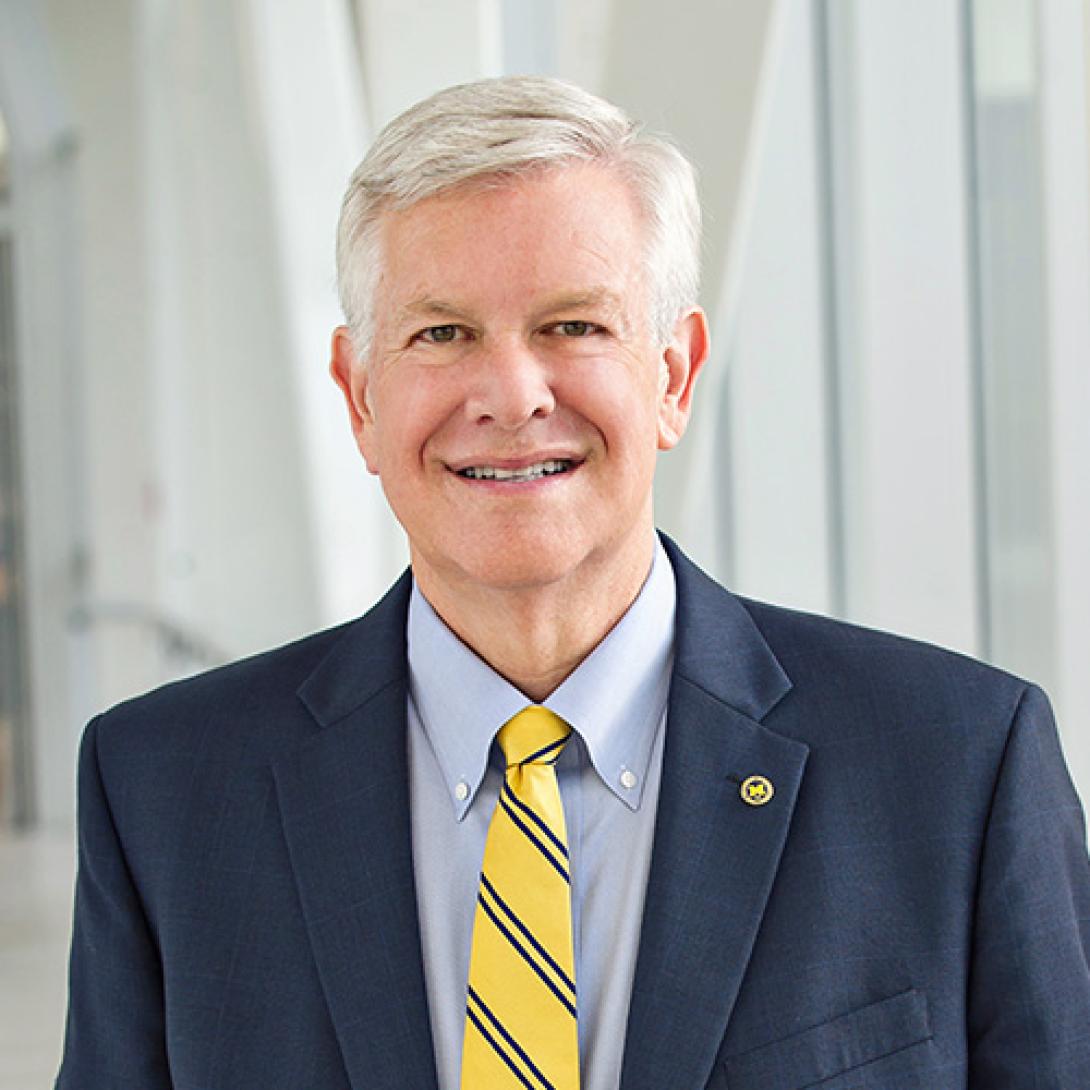

Dean, U-M Medical School
McKay Professor
Executive Vice President, Medical Affairs, University of Michigan
Chief Executive Officer, Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!