Talk to your doctor about whether taking aspirin can do you more harm than good.
11:01 AM
Author |
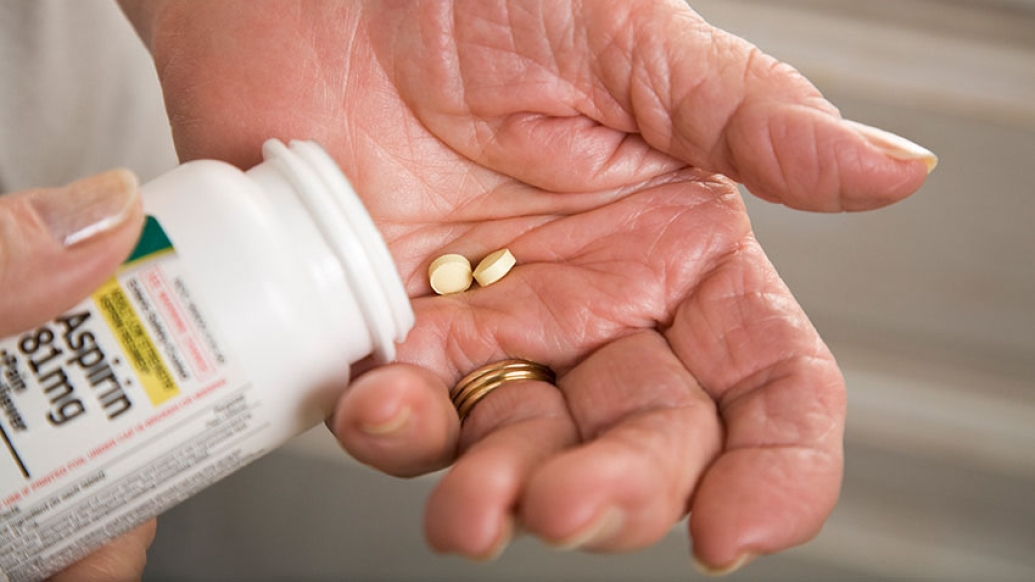

If you're already taking one blood thinner, mounting research suggests you might not need to take a second one.
In fact, when patients who are on a commonly prescribed blood thinner stop taking aspirin, their risk of bleeding complications drops significantly, a Michigan Medicine study finds.
Researchers analyzed over 6,700 people treated at anticoagulation clinics across Michigan for venous thromboembolism, or blood clots, as well as atrial fibrillation, an irregular heart rhythm that can cause stroke. Patients were treated with the common blood thinner warfarin but also took aspirin despite not having history of heart disease.
MORE FROM THE LAB: Subscribe to our weekly newsletter
"We know that aspirin is not a panacea drug as it was once thought to be and can in fact lead to more bleeding events in some of these patients, so we worked with the clinics to reduce aspirin use among patients for whom it might not be necessary," said Geoffrey Barnes, M.D., senior author of the study and a cardiologist at the University of Michigan Health Frankel Cardiovascular Center.
Over the course of the study intervention, aspirin use among patients decreased by 46.6%. With aspirin used less commonly, the risk of a bleeding complication dropped by 32.3% — amounting to one major bleeding event prevented per every 1,000 patients who stop taking aspirin. Results are published in JAMA Network Open.
"When we started this study, there was already an effort by doctors to reduce aspirin use, and our findings show that accelerating that reduction prevents serious bleeding complications which, in turn, can be lifesaving for patients," said Barnes, who is also an associate professor of internal medicine at U-M Medical School and program director of the Michigan Anticoagulation Quality Improvement Initiative. "It's really important for physicians and health systems to be more cognizant about when patients on a blood thinner should and should not be using aspirin."
These findings show how important it is to only take aspirin under the direction of your doctor and not to start taking over-the-counter medicines like aspirin until you review with your care team if the expected benefit outweighs the risk.Jordan Kendall Schaefer, MD
This de-escalation of aspirin use is based off several studies that found concerning links between concurrent use of aspirin and different blood thinners.
One study reported that patients taking warfarin and aspirin for atrial fibrillation and VTE experienced more major bleeding events and had more ER visits for bleeding than those taking warfarin alone. Similar results occurred for patients taking aspirin and direct oral anticoagulants – who were found more likely to have a bleeding event but not less likely to have a blood clot.
"While aspirin is an incredibly important medicine, it has a less widely used role than it did a decade ago," Barnes said. "But with each study, we are seeing that there are far fewer cases in which patients who are already on an anticoagulant are seeing benefit by adding aspirin on top of that treatment. The blood thinner they are taking is already providing some protection from clots forming."
For some people, aspirin can be lifesaving. Many patients who have a history of ischemic stroke, heart attack or a stent placed in the heart to improve blood flow – as well as those with a history of cardiovascular disease – benefit from the medication.
The challenge comes when some people take aspirin without a history of cardiovascular disease and are also prescribed an anticoagulant, said first author Jordan Schaefer, M.D., a hematologist at U-M Health and clinical associate professor of internal medicine at U-M Medical School.
"Many of these people were likely taking aspirin for primary prevention of heart attack or stroke, which we now know is less effective than once believed, and no one took them off of it when they started warfarin," Schaefer said. "These findings show how important it is to only take aspirin under the direction of your doctor and not to start taking over-the-counter medicines like aspirin until you review with your care team if the expected benefit outweighs the risk."
Live your healthiest life: Get tips from top experts weekly. Subscribe to the Michigan Health blog newsletter
Headlines from the frontlines: The power of scientific discovery harnessed and delivered to your inbox every week. Subscribe to the Michigan Health Lab blog newsletter
Like Podcasts? Add the Michigan Medicine News Break on Spotify, Apple Podcasts or anywhere you listen to podcasts.
Additional authors include Josh Errickson, Ph.D., Xiaokui Gu, M.D., M.A., Tina Alexandris-Souphis, R.N., Brian Haymart, R.N., M.S., Eva Kline-Rogers, M.S., R.N., N.P., Suman L. Sood, M.D., MSCE, James B. Froehlich, M.D., M.P.H., all of University of Michigan, Mona A. Ali, Pharm.D., Department of Heart and Vascular Services at Beaumont Hospital, Scott Katz, D.O., Division of Hospital Medicine at Henry Ford Hospital, Jay H. Kozlowski, M.D., Huron Valley Sinai Hospital, Gregory D. Krol, M.D.,Vinay Shah, M.D., both of Department of Internal Medicine at Henry Ford Hospital.
Support for the Michigan Anticoagulation Quality Improvement Initiative is provided by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Michigan as part of the BCBSM Value Partnerships program.
During the study, Barnes reported receiving personal fees from Pfizer/Bristol Myers Squibb and Janssen, all of whom manufacture anticoagulants.
Like Podcasts? Add the Michigan Medicine News Break on iTunes or anywhere you listen to podcasts.
"Assessment of an Intervention to Reduce Aspirin Prescribing for Patients Receiving Warfarin for Anticoagulation," JAMA Network Open. DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.31973

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!