The goal is to help primary care providers identify and treat more people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
4:00 PM
Author |
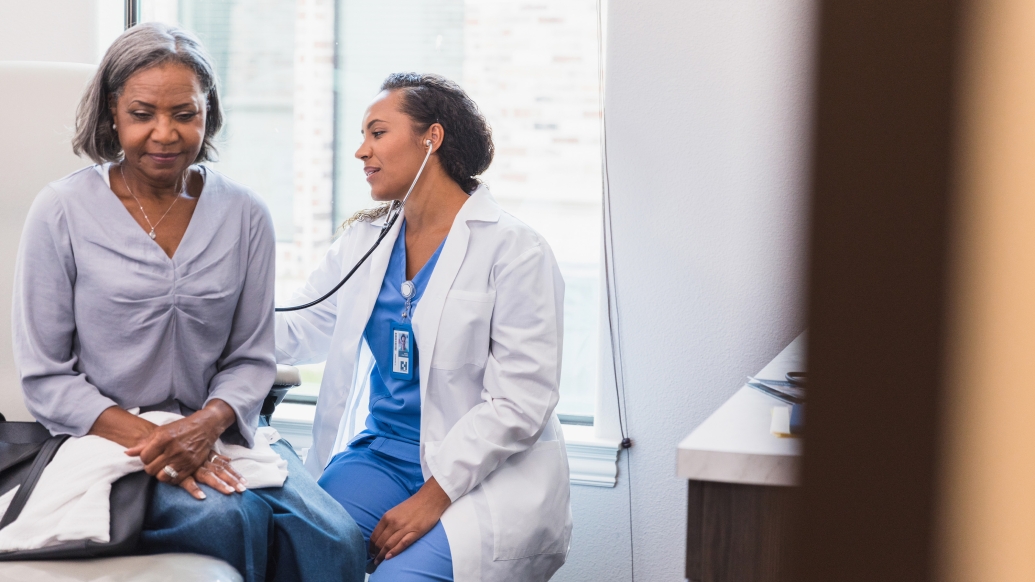

A new tool shows promise in helping primary care physicians identify adults with undiagnosed chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, according to research published in JAMA. More than 15 million Americans have been diagnosed with COPD, a leading cause of death in the United States, and experts predict millions more have it but don’t know it.
“The study shows that there is a high degree of respiratory burden in primary care, and physicians need to ask about it and do the appropriate testing to determine if symptoms are driven by COPD or another process so that patients can get the right treatment,” said MeiLan K. Han, M.D., a principal investigator of the study and chief of the Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care at the U-M Medical School.
The COPD Assessment in Primary Care to Identify Undiagnosed Respiratory Disease & Exacerbation Risk, also known as CAPTURE, developed with support from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, part of the National Institutes of Health, was designed to identify adults with COPD symptoms severe enough to treat, but who haven’t received a diagnosis. After a multi-year-long clinical trial, researchers found CAPTURE successfully identified almost half of participants who had moderate to severe forms of previously undiagnosed COPD.
“The goal with trying to find COPD is to treat it earlier, which will help make patients feel better and hopefully prevent their disease from progressing,” said Fernando J. Martinez, M.D., a principal investigator of the study and chief of the Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine division at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York City.
Conducted at seven U.S. clinical research network centers from October 2018 to April 2022, the trial involved 4,325 adults, ages 45-80. By the end of the study, researchers discovered that 110 participants, 2.5% of the study sample, had moderate to severe forms of COPD. CAPTURE identified 53, or 48%, of these cases. However, it provided false positives for 479 participants, 11%, who did not have COPD. All participants received COPD testing, which is how researchers assessed the tool’s effectiveness.
While the researchers said they are studying ways to improve CAPTURE’s accuracy, they emphasized the goal of the screening criteria is not to diagnose COPD, but to identify patients who would benefit from COPD testing. The gold standard for diagnosing the condition is through spirometry, a breathing test.
Common COPD symptoms include coughing, shortness of breath, wheezing or whistling in the chest, and chest tightness or heaviness. People with more advanced cases may experience limitations with regular activities due to increased risks for lung infections, like the flu or pneumonia, which can cause COPD flare-ups or exacerbations. Treatment options include different types of inhalers, pulmonary rehabilitation and support with quitting smoking.
As part of CAPTURE screening, which is already used by some physicians, patients answer five questions, which assess their breathing and exposure to chemicals and air pollution. Those with medium scores of 2-4, indicative of moderate breathing issues, take an in-office breathing test to measure their peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR), or the force of exhalation or lung function. Adults with PEFR scores of less than 250 L/min for women and less than 350 L/min for men get COPD testing. Those with higher questionnaire scores of 5-6 skip the PEFR test and automatically get COPD testing.
One benefit of the CAPTURE screening, the researchers said, is that it gives doctors information to further assess patients with respiratory symptoms. Doctors tend to underuse spirometry – only about a third of COPD assessments include it – in part because some find the tests difficult to integrate into shorter, primary care office visits.
“CAPTURE was designed to be easy for physicians to use,” said Antonello Punturieri, M.D., Ph.D., program director of NHLBI’s Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease/Environment Program. “The screening is simple, takes less than a minute, and helps identify adults with trouble breathing who should be evaluated further.”
Based on the researchers’ analysis, 1 in 81 CAPTURE screenings would identify an adult with treatable but previously undiagnosed COPD. Researchers are currently studying if making minor changes, like altering questions or adding others, might improve the tool’s accuracy so that even more patients with COPD can be identified. Additional studies are also needed to see if use of CAPTURE will improve patient health outcomes.
In the meantime, larger studies are underway to assess CAPTURE and how physicians use the tool in practice. Results are expected to be available later this year. The research was partially funded by NHLBI through grant 1R01HL136682.
Learn more about COPD and lung health.
Paper cited: Martinez FJ, Han MK, Lopez C, et al. “Discriminate accuracy of the CAPTURE tool for identifying chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in US primary care settings,” JAMA. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2023.0128
Live your healthiest life: Get tips from top experts weekly. Subscribe to the Health & Wellness newsletter by Health Lab
Headlines from the frontlines: The power of scientific discovery harnessed and delivered to your inbox every week. Subscribe to Health Lab’s Research & Innovation newsletter
Like Podcasts? Add the Michigan Medicine News Break on Spotify, Apple Podcasts or anywhere you listen to podcasts.

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!