Access to safe indoor isolation rooms, and outdoor activity spaces, vary by race/ethnicity and income.
9:26 AM
Author |

One of the most important ways to stop the spread of COVID-19 is for people who have tested positive, or have symptoms, to isolate themselves from the other people they live with.
But a new University of Michigan poll suggests that nearly one in five older adults don't have the ability to do this – and that those who are Hispanic or Black, or who have lower incomes or poor health to begin with, are more likely to lack a safe isolation place in their home.
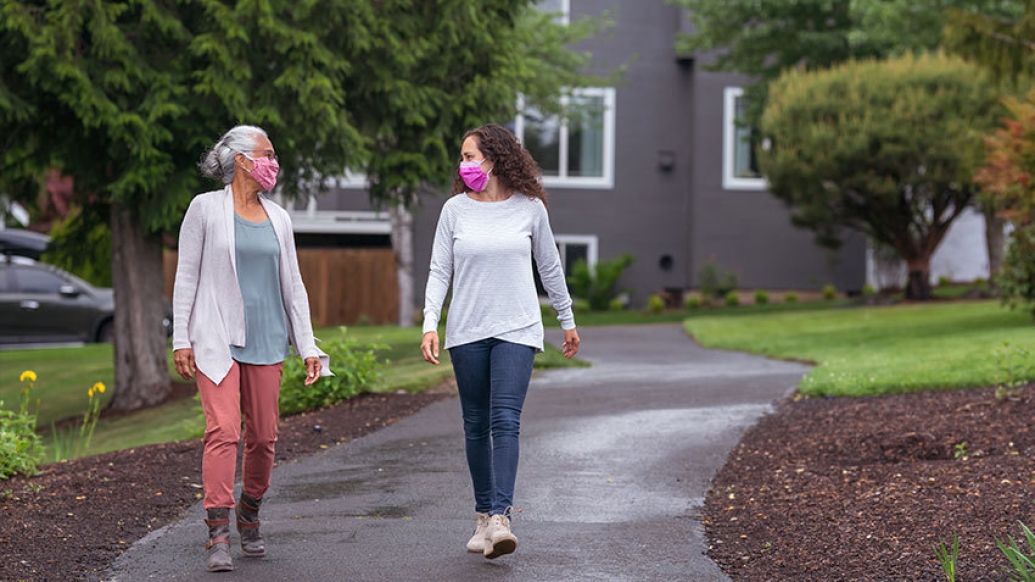
The poll also shows significant inequality in another key aspect of staying safe and healthy during the pandemic: the ability to get outside for fresh air and exercise, and to engage safely with friends, neighbors and relatives in open air.
Older adults who had more access to outdoor spaces around their home, and those who could walk to greenspaces like parks, gardens or woods, were more likely to engage in the kinds of outdoor activities and safe social connections that experts urge everyone to engage in during the pandemic. But that access also varied by income, race/ethnicity and health status.
The poll shows how important the 'built environment' of housing and local outdoor public spaces is to the health of older adults, says the team that conducted the poll as part of the National Poll on Healthy Aging, based at U-M's Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation.
The poll receives support from AARP and Michigan Medicine, U-M's academic medical center, and draws from the answers of a national sample of more than 2,000 adults aged 50 to 80.
"These findings build on what we already know about the link between a person's home and community environment, and their engagement in health-promoting activities, but through the lens of a pandemic that disproportionately affects older adults, adults of color and low-income people," says Upali Nanda, Ph.D., an associate professor in U-M's Taubman College of Architecture & Urban Planning.
SEE ALSO: Keeping Our Patients Safe During COVID-19
"In the short term, recommendations by health officials and health care providers should take these disparities into account," says Andrew Ibrahim, M.D., M.Sc., a surgeon and health care researcher at Michigan Medicine. "In the long term, architects and urban planners should see the lessons from this report as evidence that they can and should be front-line workers for the health of communities."
More about the poll findings
The ability to isolate from others in the same living space when sick with COVID-19, or known to be infected with the novel coronavirus, is critical to preventing others from getting sick. This is especially important for people who live with others who are at higher risk if they develop COVID-19, such as people over 50, people with underlying conditions such as obesity, diabetes and lung disease, and people who have weakened immune systems.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that people with the disease or a positive COVID-19 test result should isolate in a separate room, and use a separate bathroom if possible. The people who live with them should take other precautions to protect themselves.
In the long term, architects and urban planners should see the lessons from this report as evidence that they can and should be front-line workers for the health of communities.Andrew Ibrahim, M.D., M.Sc.
"Research has proven that COVID-19 can spread easily within homes, so that's why it's concerning that 18% of people over 50 don't have a way to do so, and that this rose to 27% among those who say they're in fair or poor health, which may indicate a higher risk of severe COVID-19," says Preeti Malani, M.D., the poll director and a Michigan Medicine physician specializing in geriatrics and infectious diseases. "The disparities we saw in the poll suggest differences in living arrangements may be playing a larger role in the pandemic than we thought, and point to a need for health providers and public health officials to advise the public on ways to stay safe depending on their individual living situation."
SEE ALSO: Seeking Medical Care During COVID-19
For instance, if there's only one bedroom, the infected person should isolate there, and uninfected people should sleep on a couch or mattress in the living room. Uninfected people who live with someone with a known case of COVID-19 should also quarantine, which means staying home and not going to stores, work, school or on outings – but missing work can be hard or impossible for low-income people who work independently or in frontline hourly jobs.
Nearly a third of Hispanic poll respondents (31%) said they didn't have a place to isolate in their home, compared with 25% of Black respondents and 14% of white respondents. People with household incomes under $30,000 were more than twice as likely as those with incomes over $100,000 to say they lack a safe isolation space. Apartment dwellers were more than twice as likely as those who live in single-family detached homes to say they had no place to isolate.
On the flip side of the pandemic, living arrangements can affect an older adults ability to stay positive, healthy and socially engaged during the pandemic, the poll finds. While most of the older adults said they had an outdoor space where they could safely connect with neighbors, 32% don't live within walking distance of a greenspace.
That percentage was higher for Blacks (46%) and Hispanics (50%), and for people with incomes under $30,000 (51%). There were statistically significant differences by race/ethnicity, income and health status in having a view of nature, place to safely connect with neighbors and greenspace within walking distance.
MORE FROM THE LAB: Subscribe to our weekly newsletter
"It's important that communities be livable for people of all ages, including access to work, shopping, recreation and public places," says Alison Bryant, Ph.D., Senior Vice President of Research for AARP. "Despite the documented desire of most older adults to stay in their homes and communities as they age, research from AARP has found that most older adults do not reside in highly livable communities, and there is much more that could be done to help old adults age where they currently live."
Three-quarters of respondents said they had spent time outdoors or interacted with nature at least a few times per week in the first months of the pandemic. Nearly half had walked or bicycled around their neighborhood at least a few times a week in that time, too. Those who had access to outdoor spaces and nearby greenspaces were more likely to have done so.
In addition to their U-M faculty roles, Nanda has a role with HKS, Inc., and Ibrahim has a role with HOK, both global architecture firms.
The National Poll on Healthy Aging results are based on responses from a nationally representative sample of 2,074 adults aged 50 to 80 who answered a wide range of questions online in June 2020. Questions were written, and data interpreted and compiled, by the IHPI team. Laptops and Internet access were provided to poll respondents who did not already have them. A full report of the findings and methodology is available, along with the past National Poll on Healthy Aging reports.
Like Podcasts? Add the Michigan Medicine News Break on iTunes, Google Podcast or anywhere you listen to podcasts.

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!