Urine leakage can get in the way of life and exercise; results point to potential importance of routine screening
3:06 PM
Author |

Nearly half of women over 50 say they sometimes leak urine -- a problem that can range from a minor nuisance to a major issue -- according to a new national poll.
Of more than 1,000 women between the ages of 50 and 80 who answered the poll, 43 percent of women in their 50s and early 60s said they had experienced urinary incontinence, as had 51 percent of those age 65 and over.
Yet two-thirds of these women hadn't talked to a doctor about the sometimes embarrassing, little-discussed issue. And only 38 percent said they do exercises that can strengthen the muscles that can help keep urine in.
The poll shows they're finding ways of coping on their own – from using pads or special underwear to wearing dark clothing and limiting fluid intake.
LISTEN UP: Add the new Michigan Medicine News Break to your Alexa-enabled device, or subscribe to our daily audio updates on iTunes, Google Play and Stitcher.
Not inevitable
The new findings from the National Poll on Healthy Aging suggest that more physicians should routinely ask their older female patients about incontinence issues. The poll of 1,027 women between the ages of 50 and 80, 46 percent of whom said they had experienced urine leakage, was conducted by the University of Michigan Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation, and sponsored by AARP and Michigan Medicine, U-M's academic medical center.
"Urinary incontinence is a common condition that may not be routinely screened for in primary care, yet it can impact a woman's quality of life and health, and is usually treatable," says Carolyn Swenson, M.D., a urogynecologist at Michigan Medicine and IHPI member who helped develop the poll questions and analyze the findings. "It's not an inevitable part of aging and shouldn't be over-looked."
Swenson studies delivery of women's health care, especially related to the pelvic floor – the structures and muscles that support the bladder and reproductive organs. She notes that there are non-surgical and surgical options for treating incontinence.
Of the women who said they'd experienced at least some urine leakage, 41 percent described it as a major problem or somewhat of a problem. One-third of those with leakage experienced an episode almost every day. Nearly half worried that it would get worse as they got older.
MORE FROM THE LAB: Subscribe to our weekly newsletter
The most common triggers were coughing or sneezing – experienced by 79 percent – and trying to get to a bathroom in time, experienced by 64 percent. But 49 percent said they'd leaked when laughing, and 37 percent said it had happened when they exercised.
"The last thing that older women should be doing is avoiding exercise or not being able to enjoy other activities that make life worthwhile," says Preeti Malani, M.D., director of the poll and a professor of internal medicine at the U-M Medical School who has special training in geriatric medicine. "We hope these findings will help spur conversations between women and their health care providers, so that activities aren't limited."
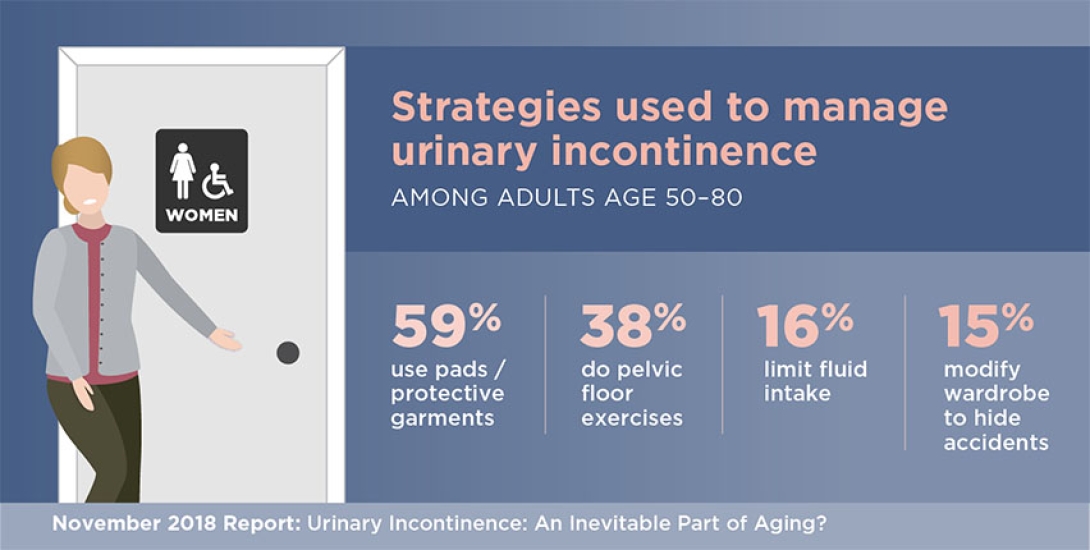
Coping strategies
Women reported doing many things to cope with incontinence, including 59 percent who said they'd bought special pads or undergarments. Sixteen percent had cut down on the amount of fluid they drink, and 15 percent said they'd changed what they wore to hide accidents in case they occurred.
But only 38 percent had done Kegel exercises, which involve squeezing and releasing the muscles of the pelvic floor. Such pelvic floor muscle exercises can be an effective treatment when done correctly and consistently, especially as part of pelvic floor physical therapy with a specialized physical therapist.
"It's both surprising and disheartening to see that so many women seem to believe that incontinence is just a normal part of aging because it's not," says Alison Bryant, Ph.D., senior vice president of research for AARP. "A lot of women are unnecessarily limiting their daily activities and not enjoying life fully because of a condition that can often be remedied."
Consulting with providers
Women older than 65 were more likely to have talked with a medical provider about their incontinence than younger women. So were women who reported being embarrassed by their urine leakage or said it was a problem for them.
Among women who didn't talk with their doctor about their urinary incontinence, 22 percent said they didn't think of urine leakage as a health problem, so they didn't discuss it with their doctor. But Swenson notes that many treatment options now exist for urinary incontinence, and that Medicare and private insurers routinely cover both medical and surgical treatments.
Swenson is part of the Pelvic Floor Disorders treatment team at Michigan Medicine's Von Voigtlander Women's Hospital, which offers a full range of treatments for urinary incontinence and other pelvic floor issues. Such treatments range from physical therapy and pessary devices to nerve stimulation, injections done in the office to prevent exercise-related incontinence, and minimally invasive surgery.
The poll results are based on responses from a nationally representative sample of 1,030 women ages 50 to 80 who answered a wide range of questions online. Questions were written, and data interpreted and compiled, by the IHPI team. Laptops and Internet access were provided to poll respondents who did not already have it.
A full report of the findings and methodology is available at www.healthyagingpoll.org, along with past National Poll on Healthy Aging reports.

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!